© 2009 - 2021 Orbit Design 290 Pratt St. Meriden, CT 06450 - Call: (203) 393-0171

Orbit Design Materials
In Orbit Design, Thermoplastic Injection Molding Is
Our Specialty
Orbit Design Works with almost every thermoplastics material in the industry. Orbit Design ability to work with these different materials developed with over 35 years of manufacturing experience. Here we leave a brief description of the materials, with which Orbit Design works daily in our plastic injection molding products.Polyimide
Polyimide (sometimes abbreviated PI ) is a polymer of imide monomers. Polyimides have been in mass production since 1955. With their high heat- resistance, polyimides enjoy diverse applications in roles demanding rugged organic materials, e.g. high temperature fuel cells, displays, and various military roles. A classic polyimide is Kapton, which is produced by condensation of pyromellitic dianhydride and 4,4'-oxydianiline.


Polycarbonate
Polycarbonates ( PC ) are a group of thermoplastic polymers containing carbonate groups in their chemical structures. Polycarbonates used in engineering are strong, tough materials, and some grades are optically transparent. They are easily worked, molded, and thermoformed. Because of these properties, polycarbonates find many applications. Polycarbonates do not have a unique resin identification code (RIC) and are identified as "Other", 7 on the RIC list. Products made from polycarbonate can contain the precursor monomer bisphenol A (BPA).
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene ( ABS ) (chemical formula (C8H8)x·(C4H6)y·(C3H3N)z) is a common thermoplastic polymer. Its glass transition temperature is approximately 105 °C (221 °F).[2] ABS is amorphous and therefore has no true melting point. ABS is a terpolymer made by polymerizing styrene and acrylonitrile in the presence of polybutadiene. The proportions can vary from 15 to 35% acrylonitrile, 5 to 30% butadiene and 40 to 60% styrene. The result is a long chain of polybutadiene criss-crossed with shorter chains of poly(styrene-co-acrylonitrile).

Polyphthalamide
Polyphthalamide (aka. PPA , High Performance Polyamide) is a subset of thermoplastic synthetic resins in the polyamide (nylon) family defined as when 55% or more moles of the carboxylic acid portion of the repeating unit in the polymer chain is composed of a combination of terephthalic (TPA) and isophthalic (IPA) acids. The substitution of aliphatic diacids by aromatic diacids in the polymer backbone increases the melting point, glass transition temperature, chemical resistance and stiffness. PPA based resins are molded into parts to replace metals in applications requiring high temperature resistance such as automotive powertrain components, the housing for high temperature electrical connectors and many other uses.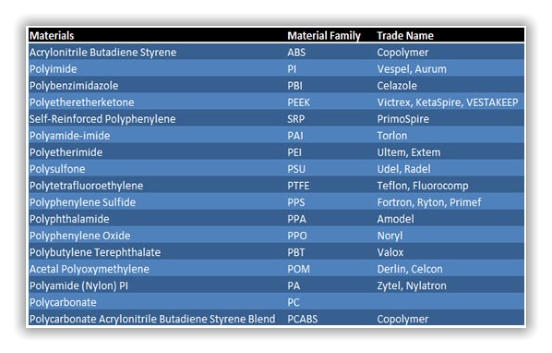
Out this World Innovation in Plastic Molding and Tooling!

© 2009 - 2021 Orbit Design 290 Pratt St. Meriden, CT 06450
Call: (203) 393-0171


Orbit Design Materials
In Orbit Design,
Thermoplastic Injection
Molding Is Our Specialty
Orbit Design Works with almost every thermoplastics material in the industry. Orbit Design ability to work with these different materials developed with over 35 years of manufacturing experience. Here we leave a brief description of the materials, with which Orbit Design works daily in our plastic injection molding products.Polyimide
Polyimide (sometimes abbreviated PI ) is a polymer of imide monomers. Polyimides have been in mass production since 1955. With their high heat-resistance, polyimides enjoy diverse applications in roles demanding rugged organic materials, e.g. high temperature fuel cells, displays, and various military roles. A classic polyimide is Kapton, which is produced by condensation of pyromellitic dianhydride and 4,4'- oxydianiline.


Polycarbonate
Polycarbonates ( PC ) are a group of thermoplastic polymers containing carbonate groups in their chemical structures. Polycarbonates used in engineering are strong, tough materials, and some grades are optically transparent. They are easily worked, molded, and thermoformed. Because of these properties, polycarbonates find many applications. Polycarbonates do not have a unique resin identification code (RIC) and are identified as "Other", 7 on the RIC list. Products made from polycarbonate can contain the precursor monomer bisphenol A (BPA).
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene ( ABS ) (chemical formula (C8H8)x·(C4H6)y·(C3H3N)z) is a common thermoplastic polymer. Its glass transition temperature is approximately 105 °C (221 °F).[2] ABS is amorphous and therefore has no true melting point. ABS is a terpolymer made by polymerizing styrene and acrylonitrile in the presence of polybutadiene. The proportions can vary from 15 to 35% acrylonitrile, 5 to 30% butadiene and 40 to 60% styrene. The result is a long chain of polybutadiene criss-crossed with shorter chains of poly(styrene-co- acrylonitrile).

Polyphthalamide
Polyphthalamide (aka. PPA , High Performance Polyamide) is a subset of thermoplastic synthetic resins in the polyamide (nylon) family defined as when 55% or more moles of the carboxylic acid portion of the repeating unit in the polymer chain is composed of a combination of terephthalic (TPA) and isophthalic (IPA) acids. The substitution of aliphatic diacids by aromatic diacids in the polymer backbone increases the melting point, glass transition temperature, chemical resistance and stiffness. PPA based resins are molded into parts to replace metals in applications requiring high temperature resistance such as automotive powertrain components, the housing for high temperature electrical connectors and many other uses.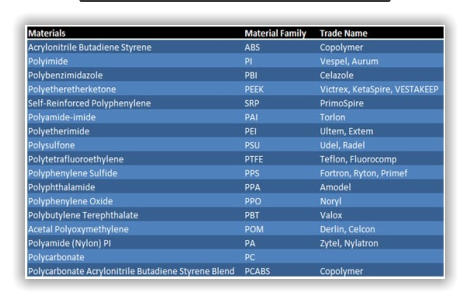
Out this World Innovation in
Plastic Molding and Tooling!